Friday Flash Card Episode 2: 10 Point To Normal Sinus Rhythm
- educatednurse1
- Aug 1
- 3 min read
Electrocardiograms (ECG or EKGs) are one of the most powerful diagnostic tools in emergency medicine. They give us a real-time picture of the electrical activity of the heart - everything from life-threatening arrhythmias to subtle ischemic changes. Yet, for many students, interpreting an EKG can be downright intimidating! This week, I'm breaking down the 10 Points To Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR). Because, once you understand "normal" - we can start to look at all the abnormal!
Know Your Basics: EKG Measurements:
P Wave: Originates at the SA node and represents passage of electrical activity through the atrium causing atrial depolarization (Always seems backwards to me, but this is atrial contraction). Time: 0.06 - 0.12 seconds (1.5-3 little boxes)
PR Interval: Measured from the beginning of the P Wave to the beginning of the QRS (should be called the PQ interval in my opinion- LOL). Represents conduction time from SA node, through the atria to the AV node, to the bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers - to a point just before ventricular contraction. Time: 0.12-0.20 seconds (3-4 little boxes)
QRS Complex: Ventricular depolarization or contraction. Time: <0.12 seconds (3 little boxes).
ST Segment: Measured from the S wave in QRS to start of T wave = time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Should be flat at baseline 0.12 seconds (3 little boxes).
T Wave: Ventricular repolarization (Again, seems backwards to me but considered the recovery phase). Should be upright and < 0.16seconds (4 little boxes).
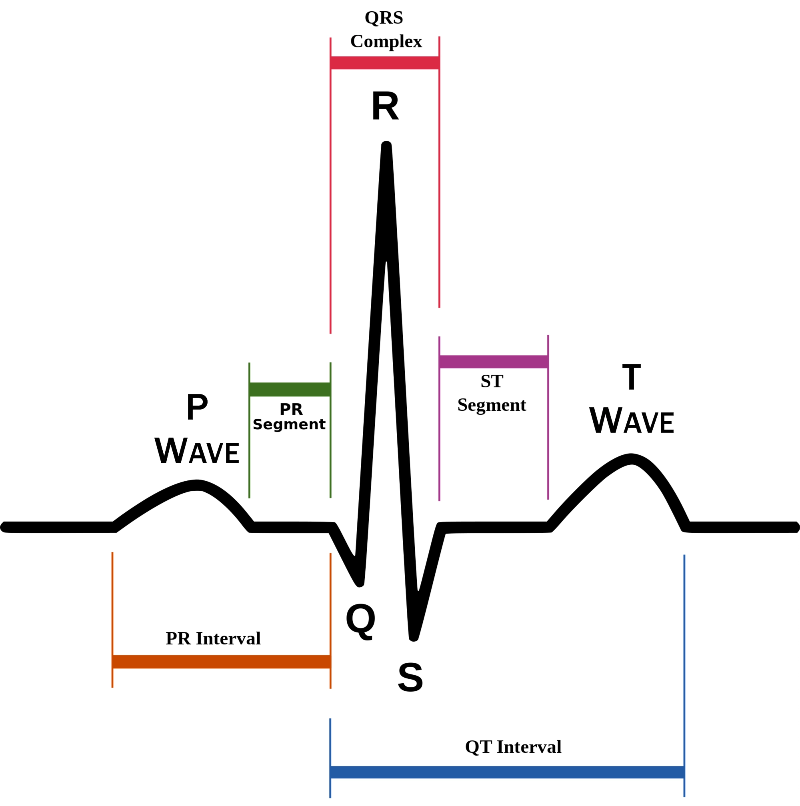
EKG Interpretation: 10 Points To Normal Sinus Rhythm
When you look at an EKG, use these 10 steps to decide if the EKG is "Normal" or not. If all 10 points are within normal limits, you can call is Normal Sinus Rhythm. If ANYTHING is abnormal, it can't be consisted normal sinus rhythm.
Rate: Should be between 60-100bpm. If it's less than <60, it's bradycardia. >100 is tachycardia. Anything outside of 60-100 = abnormal and not NSR.
Rhythm: Is it regular or irregular? Is there a pattern to the irregularity? Irregular = abnormal and not NSR.
P Waves: Are they upright and uniform? Is there one before every QRS or are there more than one? What is the measurement? If anything is abnormal = it is not NSR.
PR Interval: What is the measurement? Normal? If anything is abnormal = it is not NSR.
QRS Complex: What is the measurement? Normal? Is it narrow or wide? If anything is abnormal = it is not NSR.
ST Segment: Is it flat at baseline? Normal? Elevated or Depressed = abnormal = it is not NSR.
T Waves: What is the measurement? Is it rounded? Is it peaked? - if so, it's not normal- could indicate elevated potassium.
U Waves: Present? If so, it's not normal - can be indicative of low potassium.
Early Beats? If so = it is not NSR.
Late Beats? If so = it is not NSR.

Once you go thru all 10 steps: If it walks like a duck and talks like a duck, it's a normal sinus rhythm duck! Remember: All 10 points have to be present and normal to be NSR, if not, it can't be NSR.
Final Thoughts & Tips For Success:
Practice EKG interpretation often! The more you read, the faster you'll recognize patterns and the quicker you can rule out "the big bad scary stuff"!
Always correlate with the patient's clinical picture. A "bad looking" EKG strip doesn't always mean a crashing or unstable patient and vice versa. An EKG is just one diagnostic tool. Don't forget to do a complete history/physical, collect labs, and seek expert cardiac consultation.
Use a systematic approach each time- After >20yrs in healthcare, I still run through the 10 points, every time!
REMEMBER: Whether you're a nursing student, EMT, medic, or seasoned nurse, becoming confident in EKG interpretation can boost your clinical judgement and save lives. So, the next time that paper strip rolls out, don't panic! Follow your 10 steps - If something doesn't look right, check your patient and the leads and don't be afraid to speak up! Minutes matter - your ability to read an EKG and recognize changes could change the patient's course of care and their outcome.
Looking For More EKG Education?
Check out my You Tube Channel: I have a whole series on EKGs where I break down all the basic EKG rhythms! https://www.youtube.com/@educatEDnurse









Comments